Scientists have discovered a monumental ‘weak spot’ in our planet’s magnetic field is growing, which could have huge consequences for us on Earth.
Space is constantly changing, with NASA focusing many of their attentions on the ‘city-destroying’ asteroid these days.
But that doesn’t mean the space agency isn’t working on other things behind the scenes, and it was revealed earlier this year that NASA had been alerted to a huge ‘dent’ in Earth’s magnetic field that could prove dangerous to both biological and mechanical production.
The discovery has scientists concerned (Getty Stock Photo)
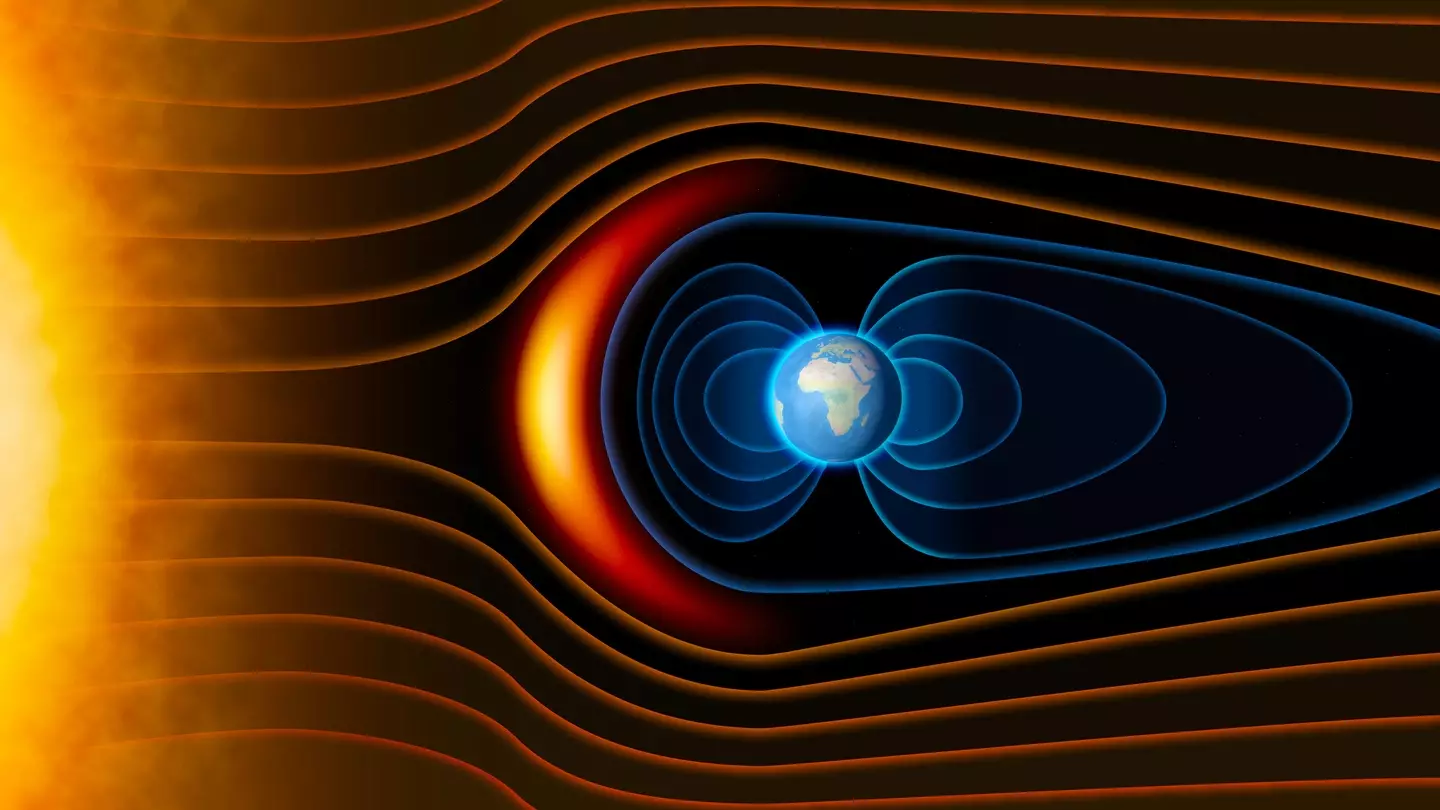
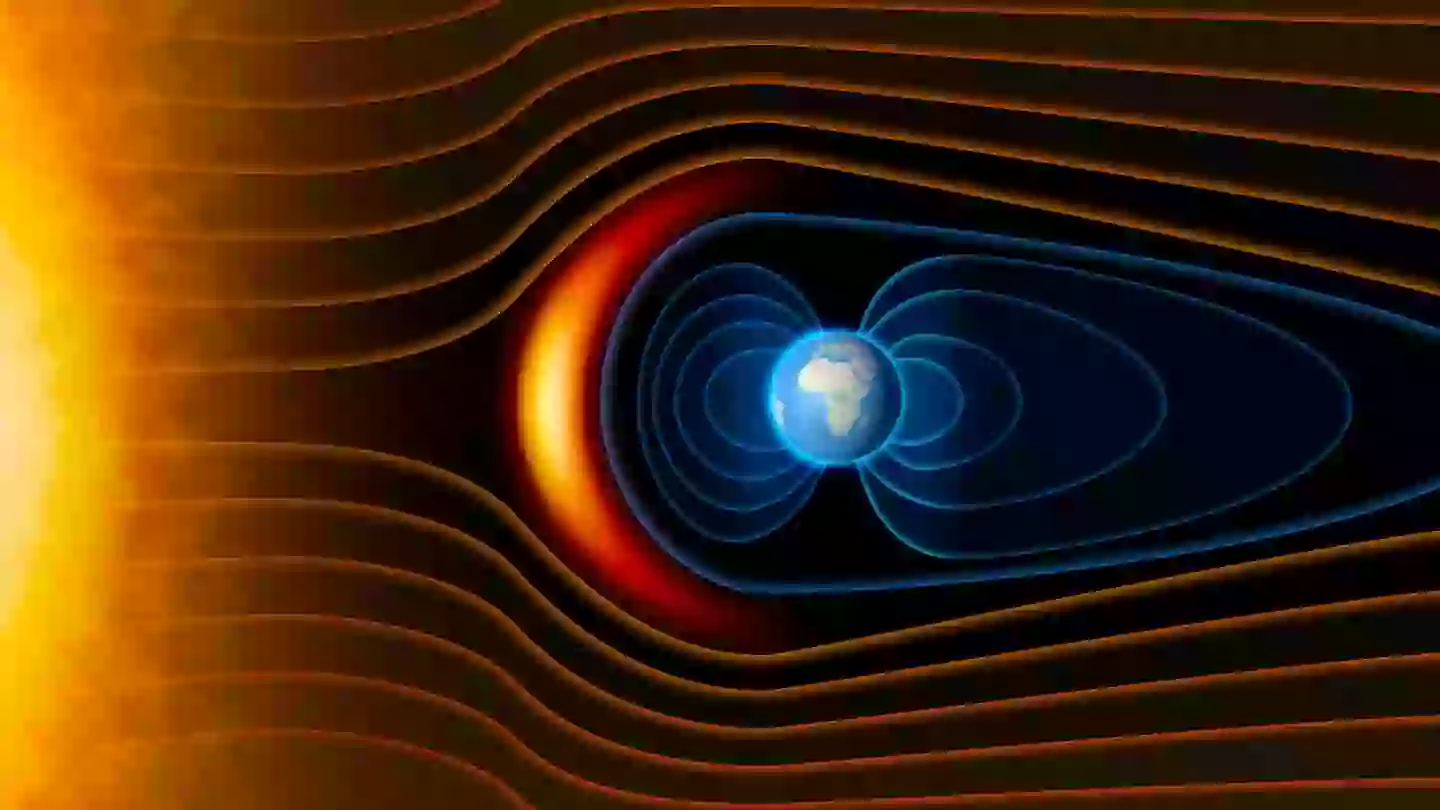
The massive ‘weak spot’ could potentially allow dangerous radiation from the Sun to penetrate the surface of our planet, according to NASA.
The area of which the discovery has been made is known as the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA), and it stretches around 4,300,000 square miles across an area that encompasses the continents of South America and Africa.
It’s believed this SAA has expanded by around seven percent since it was discovered in 2020, though experts have seen a ton of changes in it ever since.
Scientists say the SAA has shifted from a single zone into two separate ‘blobs’ that compromise Earth due to limited magnetic strength.
Earth’s magnetic field is extremely crucial, as it prevents dangerous radiation from the Sun that would prove harmful to biological life on the surface.
You’ve also got the impacts on technology, with damage to satellites in orbit right now potentially disabling computer signals and compromising satellite data collection.
Terry Sabaka, a geophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, said: “Even though the SAA is slow-moving, it is going through some change in morphology, so it’s also important that we keep observing it by having continued missions, because that’s what helps us make models and predictions.”


NASA are closely watching things (NASA)
It comes as the space boffins over at NASA continue to look closer into the ‘city-destroying’ asteroid that could hit Earth on December 22, 2032.
As for where it’ll hit the Earth, David Rankin, who works as an operations engineer for the University of Arizona’s Catalina Sky Survey, mapped out a ‘risk corridor’, predicting it to collide anywhere around northern South America, across the Pacific Ocean, southern Asia, the Arabian Sea, and Africa.
That would mean that India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Ethiopia, Sudan, Nigeria, Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador would be at risk of taking the brunt of the impact.